Continual Process Improvement Management
Description/Summary
Continual Process Improvement Management deals with any kind of Process Design, and with implementation and improvement to the IT infrastructure and service processes. A well-defined and controlled process leads to the effective handling of Continual Process Improvements. Continual Process Improvement Management is triggered every time a request for Continual Process Improvement is received from one of the various processes: auditing activities, customer requests via CRM Management Process, or regular base auditing of other processes. Follow up activities from Process Improvement are: Process Design and Documentation, Transition and Operation, Permanent Control, and Report and Improvement.
Objectives
The purpose of Continual Process Improvement Management is to establish standardized processes for the handling of IT-related services and infrastructure, and to document, operate, control and improve them permanently.
The main purpose of Continual Process Improvement of IT Related Processes is to optimize the IT service and infrastructure processes permanently, so that best cost/ value to both company and customer can be obtained.
Continual Process Improvement Management contributes to an integrated Service Management Approach by achieving the following goals:
- Every Service Management Process is designed, tested, operated and permanently improved.
- Every Continual Process Improvement Process runs through a set of standardized activities and procedures in order to ensure effective and efficient processing.
- Every Continual Process Improvement Process that could mean a risk to normal service operation is carefully assessed and then sufficiently tested. This is done in order to avoid service disruption or degradation of service quality, in particular in terms of SLA deviations.
- Every implemented or improved Service Process is documented and reviewed.
Roles & Functions
Continual Process Improvement Management specific roles
Static Process Roles
See Continual Process Improvement Management section, Service Management Roles x Person for details
- Continual Process Improvement Process Owner
- Initiator of the process, accountable for defining the process strategic goals and allocating all required process resources. See Continual Process Improvement Management for a detailed description of these activities.
- Continual Process Improvement Process Manager (Continual Process Improvement Manager)
- Manager of the entire process, {responsible en} for its effectiveness and efficiency. Team leader of the function „Continual Process Improvement Management Team“. See Continual Process Improvement Management for a detailed description of these activities.
- Continual Process Improvement Management Team
- Team associated to the Continual Process Improvement Management Process.
- Senior Management
- Senior Management of the IT provider
Dynamic Process Roles
These roles are dynamically created during the Continual Process Improvement Management Process. See the process-specific or activity-specific rules for more details.
- Continual Process Improvement Owner
- The attribute in the records contains the value of the Role/Function currently accountable for the Continual Process Improvement (but NOT for the Continual Process Improvement Management Process). The Continual Process Improvement Owner can be Continual Process Improvement with the help of a Hierarchical Escalation.
- Continual Process Improvement Agent
- The attribute in the records contains the value of the Role/Function currently {responsible en} for either an activity or task within the overall activity of the Continual Process Improvement. The Continual Process Improvement Agent can be Continual Process Improvement with the help of a Functional Escalation, if permitted by the Rules.
- Continual Process Improvement Authority (PIA)
- The authority (person or group) authorizing a (Continual) Process Improvement. Continual Process Improvement Authorities vary depending on the Continual Process Improvement category. See the Activity Specific Rules in the activity Continual Process Improvement Classification for details.
- Continual Process Improvement Requester (PImpR)
- This is the person who triggers a Continual Process Improvement via a Request for Continual Process Improvement (RFC) form. This can be identical with a service or customer specific role.
Service Specific Roles
Roles depending on the affected service are found in the Service Description. The Service Description, including the service specific roles, are delivered from the Service Portfolio Management.
Example: Service Description
- Service Expert/Service Specialist
- They can consult and/or act as
- (Continual) Process (Improvement) Builder
- (Continual) Process (Improvement) Tester
- (Continual) Process (Improvement) Implementer
- Service Owner
Customer Specific Roles
Roles depending on the affected customer(s) are found in the Service Level Agreement (SLA). The Service Level Agreement for the customer specific roles is maintained by the Service Level Agreement Management.
- Customer(s)
- Customers of the affected Service with a valid SLA
Example: Service Level Agreement Management
Information artifacts
This section describes information/data required or recorded by the process. In general, a Process Record (here: the Continual Process Improvement Record) represents the current progress of a process and will contain all information related to the execution of that process.
Continual Process Improvement Record
Definition
The Continual Process Improvement Record is the record holding any management-relevant information and history of a specific process.
- Unique identifier
- (Continual) Process (Improvement) ID
- (Continual) Process (Improvement) requester
- Name of the Person triggering the Continual Process Improvement or the initial process design
- Process instance
- Unique Identifier of the Process Instance triggering the Continual Process Improvement Management Process. This can also be a Continual Process Improvement Instance.
- Status
- Status of the Continual Process Improvement. This is set when passing a Control Activity
- Services
- Service(s) affected by this Continual Process Improvement
- Customer
- Customer(s) affected by this Continual Process Improvement
- Continual Process Improvement Description
- The description of the Continual Process Improvement including the Continual Process Improvement Argument
- Process Information
- * Process Objective
- * Process Objects
- * Process Inputs
- * Process Outputs
- * Process Roles
- * Process Flow Description
- * Process Values and Arguments
- * Process Detailed Description
- * Process KPIs, metrics and performance measurement methods
- * Process CSF
- Continual Process Improvement Builder
- Date and implementation time of the (Continual) Process (Improvement)
- Implementation Plan
- Project Plan including concrete working instructions and time schedule
- Implementation Plan test results
- True or False
- Fallback Plan
- Fallback Plan including concrete working instructions and trigger for fallback
- Fallback Plan test results
- True or False
- Post Implementation Review results
- True or False
- Additional Remarks
- Text for additional information
Continual Process Improvement Record attributes x activity matrix
For icon descriptions see Record attributes X activities
Key Concepts
Basically the ITIL methodology facilitates the process orientation and thinking to the IT organization and processes. All key concepts applying for the ITIL apply to the Continual Process Improvement Management Process. Some of these concepts focus the main ideas:
- Business alignment of the processes: Market and business organization are a key orientation of IT processes and sources.
- Process first: Business Process Improvement (BPI) Process may result in technological upgrading, automation or staff reduction, although this does not necessarily mean BPI will always lead to automation / IT budgeting.
- Customer focus: Customer is the starting point of each optimization and process, and is the final optimization orientation
- Benchmarking of processes and methods: Improvement of an organization through the orientation on other organizations and organization parts.
- Role orientation: Establishes who owns, operates, improves and audits a business process
- Right measures: Concentrate on a small number of central KPIs
Process
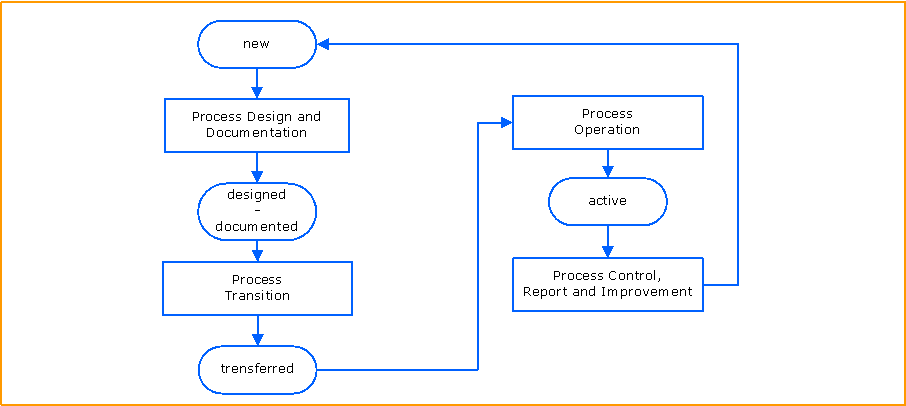
High Level Process Flow Chart
This chart illustrates the Continual Process Improvement Management process and its activities as well as the status model reflected by the Continual Process Improvement Record evolution.
Critical Success Factors
Critical Success Factors (CSF):
- An understanding of the need for Continual Process Improvement
- Resources for Continual Process Improvement
- Transparency of Continual Process Improvement resources and responsiblities
Performance Indicators (KPI)
- Number of audits completed per time period
- Number of improvements proposed
- Number of improvements implemented
- Customer satisfaction before and after process improvement
- Number of incidents/ problems before and after process improvement
per service, per user, per customer, per location, per category, …
Process Trigger
Event Trigger
- Any request for Continual Process Improvement, either:
- from any Service Management Process
- from customer via CRM Process
- Any control or audit activity that requests Continual Process Improvement
For more information see the relevant Process Interface Description in the Process Interfaces Overview
Time Trigger
- Regular process audits
Process Specific Rules
- every request for Continual Process Improvement triggers the creation of a new Continual Process Improvement Record
- the Continual Process Improvement Agent is responsible for documenting each activity in the Continual Process Improvement Record
- the Continual Process Improvement Owner has to control the Continual Process Improvement Agent
- the Continual Process Improvement Owner has to approve every process change
- the Continual Process Improvement Owner has to control if the Process Manager follow the authorization rule for new processes
- the Continual Process Improvement Owner and Continual Process Improvement Agent can only transfer their duties if the new person or group agrees
- the subsequent Continual Process Improvement Owner or Continual Process Improvement Agent must then be recorded in the appropriate attribute in the Continual Process Improvement Record
- the Continual Process Improvement Owner and Continual Process Improvement Agent should preferably be a person rather than a group
- refer to the Service Description and Service Level Agreement in order to take service specific and customer specific rules into account
Note: for the different types of rules see Rules.
Process Activities
Process Design and Documentation
A request for Continual Process Improvement or Initial Process Design needs to be verified for:
- the correct authorization of the requester to provide process (re-)design work AND
- for the request’s completeness and formal correctness; i.e. it is verified that all mandatory information has been provided by the requester through the RFC form, with respect to the desired Continual Process Improvement.
If this is not the case for one above, then the request can be rejected.
The Continual Process Improvement Record is then shifted into the status „recorded-accepted“, „recorded-emergency“ or „recorded-rejected“.
In any other case the process is designed. The process design is based on diverse sources and working approaches, which include:
- adaptation of best practices provided by benchmarks, specialists, a service provider etc.
- the creative work of individuals or teams
- other
The Continual Process Improvement Record is then shifted into the status „designed-to be approved“.
Process (re-)design needs to be approved by diverse stakeholders:
- operative resources are to approve the effectiveness and efficiency of the process
- support resources are to approve the implementation ability of the process
- the supplier is to approve the implementation ability of the process
- senior management is to approve the process
Within the process design, an approval for a broad range of resources is integrated:
- senior management approve the process and buy in
- effected resources and organizational parts for the definition of own working processes
- effected supplier and pilot customer to provide support and insights
- experts are to manage the design process and provide expertise
The Continual Process Improvement Record is then shifted into the status „designed -approved“.
Finally the process needs to be documented. Documentation tools and methods vary but it is necessary to record the following information:
- process purpose
- process description
- process resources
- process interfaces
- process versions/ ID
- process KPIs
- process requirements for tools and resources
The Continual Process Improvement Record is then shifted into the status „designed -documented“.
Activity Specific Rules
- Continual Process Improvement Requester is set to the person who triggered the Continual Process Improvement.
- Continual Process Improvement Sponsor is set to the person who triggered the Continual Process Improvement, if no other sponsor is known.
- Continual Process Improvement Agent is set to „Continual Process Improvement Management Team“ if there no person is available as the Continual Process Improvement Agent.
- Continual Process Improvement Owner is set to „Continual Process Improvement Management Team“ if there is no person available as Continual Process Improvement Owner.
- Continual Process Improvement Description The RFC must contain a meaningful description of the desired Continual Process Improvement as well as a comprehensible rationale stating the reasons for the Continual Process Improvement.
- Process Instance which triggered the Continual Process Improvement This should refer to the respective Process Instance e.g. Unique Identifier of the Incident (see also possible triggers of the Continual Process Improvement Management Process).
- Affected Service At least one service must be defined.
- Continual Process Improvement Builder At least one person from the Service Expert or Service Specialist Groups must be set as Continual Process Improvement Builder. This can be a group of experts/specialists if more then one service is affected.
Process Transition
The aim of this activity is to transfer a designed, approved and documented process into real life operations. The transition of a process into real life operations is similar to the transition of a system or service into operations. There are several tests which need to be defined, specified and processed:
- Testing of process steps
- Testing of the whole internal process
- Testing of the whole internal process, including external partners and the pilot customer
- Testing of supporting tools and resources
- Integration test of all components
- Integration test of the process, including all enablers in cooperation with other company processes and systems
After approval of all testing situations, the process needs to be transferred into operations. This means a Change Process for Processes needs to be started:
- Implementation plan needs to be defined and communicated
- Service Transition and Operation Processes need to be involved
- Fallback scenario needs to be defined
- Implementation and resources need to be scheduled
- Implementation needs are to be fulfilled.
After a defined time after an implementation, the process is declared as being up and running.
Activity Specific Rules
- Define testing scenarios
- Test the process
- Set the process record to „tested“
- Define implementation planing
- Implement the process
- Set the process record to „operating“
Process Operation
This activity enables the process to operate according to KPIs, which were set in the process definition phase and documented in the process record. The Process Manager is responsible for the process operations.
Activity Specific Rules
- check process quality by checking the process KPIs
- inform Process Improvement Activity of any KPIs below the accepted variance level
Process Control, Report and Improvement
In this activity, all processes are controlled permanently and reviewed on a regular basis. This activity cooperates with the Event & Alter, Incident, Problem, Supplier and CRM Management.
The defined KPIs are checked and controlled in the Process Definition Record and variance levels are set for each KPI. In the case of control values below the variances, the process design activity is called to where counter actions are defined.
Activity Specific Rules
- monitor processes
- in case of issues – inform process design activity