Capacity Management
Description/Summary
Information Capacity Management is dealing with the implementation and monitoring of a predefined Capacity level for the IT environment. Capacity management is balancing the requested level of capacity by customer with the operating resources and planned resources. Capacity analysis as starting point, based on Service definitions, SLAs and patterns of business activity (PBA) helps to define the customer requirements on Capacity level. Internal, minimal Capacity requirement is named IT basic capacity level. Additional Capacity requirements of the customer has to be defined on individual base.
Basic constrain of the capacity is to keep required SLAs balanced with reasonable costs and efforts.
Objectives
To introduce and maintain a required level of Capacity, as defined by the customer and senior management.
Information Capacity Management contributes to an integrated Service Management approach by achieving the following activities:
- Identifying and defining the internal and external Capacity requirements
- Planning of Capacity procedures
- Developing the Capacity Plan
- Creating a Capacity chapter in the SLA and Service Description
- Managing the implementation of Capacity actions
- Application sizing
- Evaluating the Capacity procedures and Capacity measures (including analysis of capacity peeks)
- Capacity Reporting
- Capacity Improvement
- Maintaining a Capacity Database (CDB)
Roles & Functions
Capacity Management specific roles
Static Process Roles
- Capacity Process Owner
- Capacity Process Manager
IT Capacity Management Process is controlled by the Capacity Manager. Capacity Manager can delegate tasks to specialized staff. Should it be necessary to use external staff, an approval of the budget responsible person is necessary.
- Capacity Management Process Staff
Staff in Capacity Management is performing mandatory tasks for the Capacity Manager.
Dynamic Process Roles
- Capacity Auditor
Capacity Auditor is providing the verification of capacity plan. Auditor should be altering an external and internal resource to provide independent and reliable audit.
Service Specific Roles
Roles depending on the affected service are found in the Service Description. The Service Description including the service specific roles is delivered from the Service Portfolio Management.
- Service Expert/Service Specialist
- Service Owner
- Service User
Customer Specific Roles
Roles depending on the affected customer(s) are found in the Service Level Agreement. The Service Level Agreement for the customer specific roles is maintained by the Service Level Agreement Management.
- Customer(s)
- Customers of the affected Service with a valid SLA
Information artifacts
Capacity Plan
Set of targets, measures, reports and actions to establish, maintain and audit certain level of Capacity for a set of IT services for a certain time frame (year etc.)
The Plan describes the currently available capacity and the expected changes in the demand for IT services.
Capacity Design Record
- Capacity Design ID
- Capacity Design Requester
- Capacity Design Description
- Capacity Design Agent
- Capacity Design Owner
- Service: The Service which has to be (re)designed
Capacity Transition Record
- Capacity Transaction ID
- Capacity Transition Requester
- Capacity Transition Description
- Capacity Transition Agent
- Capacity Transition Owner
- Service: Services affected by the Change
- Configuration Items: CI affected by the Change
Key Concepts
Capacity Controls
Capacity Data Set for Design
- Responsible persons
- will be defined out of the group of Capacity responsible staff
- RFC
- Interface to Change Management
- Status
- Comment
- Service out of the service catalogue
- Interface to the Service Level Management. If service is known, all further parameters like service responsible person and expert group are known
- Capacity Requirements
- Description what needs to be changed at the defined service
Life Cycle of Data Set for Design
Capacity Data Set for Implementation
- GUID
- Responsible persons
- will be defined out of the group of Capacity responsible staff
- RFC
- Interface to Change Management
- Status
- Comment
Life Cycle of Data Set for Implementation
Capacity Data Set for Validation
Life Cycle of Data Set for Validation
Capacity Data Set for Maintenance
Life Cycle of Data Set for Maintenance
Capacity Data Base (CDB)
The CDB contains technical information, business information, service related data and financial information relevant for Capacity Management. This information is basis for the management reports, capacity plan and technical reports.
Demand Management
aims to influence the demands for capacity
- short term
- long term
Performance Management
analysis, monitoring, tuning and implementing of CIs/Services via Change Management
Application Sizing
considers the hardware needed to run new or changed applications
Modeling
is used to forecast the behavior of the infrastructure
- Trend analysis
- Analytical Modeling
- Simulation Modeling
Process
Critical Success Factors
Critical Success Factors (CSF) define a limited amount of factors influencing the success of a process. For the Capacity Management following factors can be defined as CSF:
- Right dimension of Capacity avoiding overcapacity or capacity leaks
- Management support for Capacity issues
- Capacity awareness in the company
- Definition of responsibilities between Capacity implementation and Capacity control activities and roles
- Strong collaboration with customer and other service delivery processes
- Exact and opportune analysis of capacity needs and actual level
- Knowledge of state-of-the art technology, tools and methods
- Acknowledgment of IT-strategy
Capacity Manager has to regard the CSFs and to define and implement measures to fulfill the process success.
Capacity Planning
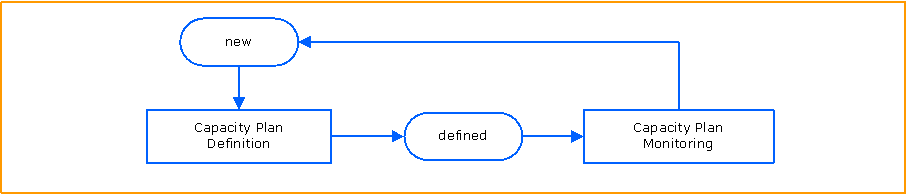
High Level Process Flow Chart
This chart illustrates the Capacity Management Planning process and its activities.
Performance Indicators (KPI)
- Number of changes to Capacity plan
- Number of capacity problems
Process Trigger
Event Trigger
Time Trigger
Process is triggered periodical.
Process Specific Rules
- Each Change to the Capacity Plan has to be documented
- Each Change to the Capacity Plan has to be published
Process Activities
Capacity Plan Definition
Capacity Plan Definition is dealing with definition of
- Basic capacity plan
Activity Specific Rules
- Capacity Manager is set to the person who responsible for availability process
- Capacity Management Team is set persons who are staff involved in availability assurance activities
- The Capacity Plan is defined:
- add new rules
- modify existing rules
- delete expired rules
Capacity Plan Monitoring
Capacity Plan Monitoring is responsible for the monitoring and update of availability planing.
Activity Specific Rules
- Communicate Capacity Plan
- Assure that staff understands and follow rules by auditing and teaching staff
- trigger updates of the Capacity Plan if necessary
Capacity Design Assistance
Sub process Design in Capacity Management is responsible for the initial planning or planning of optimizations of the Capacity process. If a change proposal on Capacity process is classified the change needs to be planned as well. This sub process is triggered by Service Design. Actions aiming the improvement of Capacity need to be documented in a Capacity Design Record document in detail. Potentially other process can provide input for the Capacity planning as well. After the planning of Capacity measurements is finished the status needs to be changed to ‘‘designed.
The process is dealing with three areas:
- Business Capacity Management:
- trend, forecast, model, prototype, size and document future business requirements
- Service Capacity Management:
- monitor, analyze, tune and report on service performance, establish baselines and profiles of user of services, manage demand for services
- Resource Capacity Management:
- monitor, analyze, run and report ob the utilization of components, establish baselines and profiles of use of components
Process owner is the Capacity Manager. Process agent is an expert assigned by „Capacity Staff“.
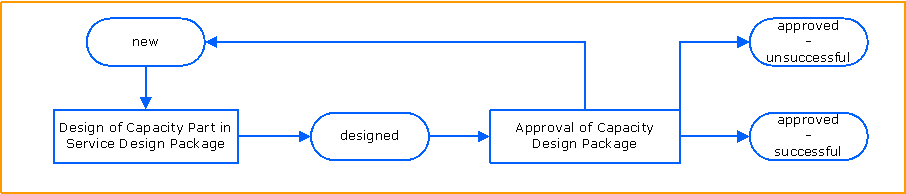
High Level Process Flow Chart
This chart illustrates the Capacity Management Design process and its activities.
Performance Indicators (KPI)
- Number of Capacity Incidents
- Number of Capacity Design Change Requests
- Number of Changes to increase Performance
- Benchmarks of capacity
- Alarms and other values of monitoring
Process Trigger
Event Trigger
The process is initiated by Change Management
Time Trigger
Process Specific Rules
- Each Capacity Design assistance Request must be recorded
- The Capacity Design Agent has to document the request and result of the design request
- The Capacity Design Owner has to control the Agent
- The Capacity Design Agent has to coordinate his work with other Design Agents
- The Capacity Design Requester has to be informed
Process Activities
Design of Capacity Part in Service Design Package
Within this activity the Capacity section of the service design package is defined.
Activity Specific Rules
- Set the Capacity Design Owner to a member of the IT Capacity Management Staff
- Set the Capacity Design Agent to a member of the Service Expert or Specialist Group
- Design Capacity according to the Capacity Plan
- Coordinate Capacity Design package with the activity „Capacity Design“ and other relevant Service Designer
- Document in the Service Design package and fill out the Capacity Design Record
- Go to control activity „designed“
Approval of Capacity Design Package
With this activity the Capacity Manager decides on the Capacity Design Package. His decision is based on the cost expectations and the Capacity Definition. In general three results of this activity are possible:
- Capacity Design Package is finally neglected
- Capacity Design Package is temporary refused and returned to the Capacity expert, for the improvement or optimization of the Feasibility Study
- Capacity Design Package is accepted.
The acting agent and the task owner is the Capacity Manager
Activity Specific Rules
- Set the Capacity Design Agent to Capacity Manager
- Approve the Capacity Design Package and Documentation in the Capacity Design Record
- On approval go to activity „approved – successful“
- else
- Go to control activity „new“ for a re-design of the Capacity Design Package OR
- Go to control activity „approved – unsuccessful“ for final abortion.
Capacity Transition Assistance
This activity, in cooperation with Change Management, is supporting the implementation and testing of Capacity improvements by designing, testing, implementing and testing the implementation again. This actions are headed by Change Management.
If a Capacity improvement is authorized and approved by Change Management, all actions functional descriptions and implementation procedures described in the improvement proposal need to be detailed, tested and approved in cooperation with the Change Management. Afterwards the implementation should be assisted to provide help in case of emergency or implementation issues.
Final PIR, conducted together with Change Management is also including testing.
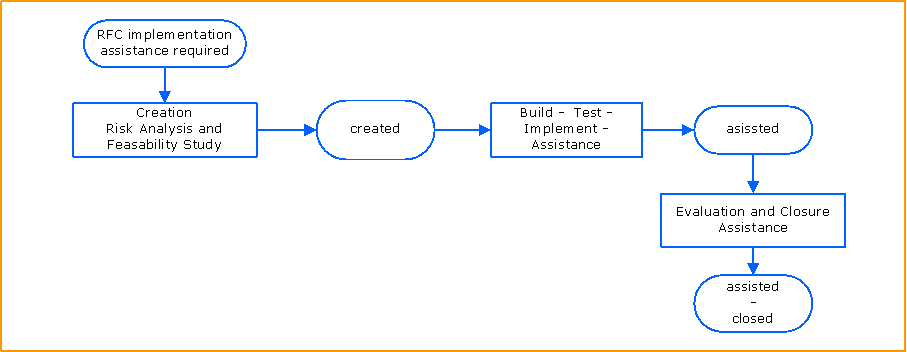
High Level Process Flow Chart
This chart illustrates the Capacity Management Transition process and its activities.
Performance Indicators (KPI)
- Overall capacity of service
- Overall usage of capacity
- Number of Capacity Transition Assistance Request
- Throughput time (min/average/max) for a Transition Assistance Request until „assisted – closed“
Process Trigger
Event Trigger
Process to be triggered by Change Management
Time Trigger
Process Specific Rules
Process Specific Rules
- Each Capacity Transition Request request must be recorded
- Capacity Transition Assistance Agent has to document the request and the result
- Capacity Transition Assistance Owner has to control the agent
- Capacity Transition Assistance Agent has to coordinate his work with other Capacity Agents
- Capacity Transition Assistance requester has to be informed on transition status
Process Activities
Creation Risk Analysis and Feasibility Study
If a capacity transition assistance is requested by Change Management the following 2 artifacts need to be defined:
- Feasibility Study
- Risk Analysis
Following aspects need to be addressed within a Feasibility Study:
- Feasibility of proposal
- Risk of implementation
- Risk of neglecting proposal
- Costs
Feasibility Study is based on high level planning and should not addressed detailed planning due to the possibility that the proposed change will not be accepted. Detailed planning of the proposal is part of the Implementation sub-process.
Feasibility Study is provided by the expert team of the address service. Eventually additional requirements need to be regarded that are provided by other like Financial, Availability or Incident Management.
Activity Specific Rules
- Set the Capacity Transition Owner to a member of the IT Capacity Management Staff
- Set the Capacity Transition Agent to a member of the Service Expert or Specialist group
- Create a Capacity Feasibility Study and Risk Analysis according to the Change Requirements and the Capacity Plan
- Coordinate the creation of the Capacity Feasibility Study and Risk Analysis package with others
- Document Capacity Feasibility Study and Risk Analysis in the Capacity Transition Record
- Go to activity „created“
Build – Test – Implement – Assistance
If a Capacity change is approved for the implementation Change Management is assigning Capacity Management respectively the sub-process Build – Test – Implement – Assistance for
- Detailed definition of implementation instructions for the Capacity improvement,
- Detailed definition of test procedures and documents for the Capacity improvement,
- Support of implementation,
- Testing of implementation and
- Approval of the implementation
For all activities above detailed documents are necessary.
Within the documentation of the improvement proposal, the order and time line of actions need to be described. Testing documentation hast to address the test design and assure effectiveness of the test.
Implementation activities are fulfilled and headed by Change Management – Capacity Management is only assisting and supporting regarding the Capacity aspects and functions. Capacity Management can be defined as agent by Change Management for some implementation steps.
The Test is split up in two main test areas:
- 1. Test of the implementation – „Does the provided document describe the right implementation actions in the right implementation time order?“
If this test is positive, then
- 2. Test of the functionality of live-system – „Does the system perform the functions defined in Design sub-process?“ This test in performed based on the defined testing documentation. This test is addressing the test design and the test effect.
If both testing areas (see above) are positive, the data set is set in status enabled. The Change Management needs to be informed on the positive result of the testing and the data set status needs to be changed to waiting. In case of negative test results, the testing can be aborted (test status needs to be set on canceled) or transferred again in the activity consolidation.
This activity is performed by expert staff assigned by Capacity Staff. Activity owner is the Capacity Manager
Activity Specific Rules
- Support creation of implementation plan including fallback plan
- Support creation of test plan
- Support test of implementation including fallback plan
- Support implementation
- Document test and implementation results
- Coordinate work with Change Management
- Go to activity „assisted“
Evaluation and Closure Assistance
In coordination with the Post Implementation Review of the Change, Capacity Management helps to test the implementation from the capacity point of view. In cases of a failed tests, the Change Management has to decide if the fallback plan has to be executed or the implementation can be accepted despite any issues in testing.
Activity Specific Rules
- Support post implementation review and test
- Consult Change Management on Fallback Execution
- Support fallback implementation if necessary
- Document activities
- Go to activity „assisted – closed“