Reporting Management
Description/Summary
Reporting Management deals with any kind of Reporting of IT infrastructure and services. A well-defined and controlled process leads to the effective handling of these reports. Reporting Management is triggered every time a request for reporting is received from one of the various processes, from a requester or from an auditor. Reports are also regularly provided.
Each request for Reporting is classified by determining its priority and urgency. In the case of requests for first time reports, the responsible Reporting Authority will decide on whether to approve or dismiss the request. Reporting Management coordinates all incidental tasks within the context of ‚Reporting building, testing and release‘. Close collaboration between Reporting Management and Service Management is important for the success of this process.
Objectives
The purpose of Reporting Management is to establish standardized procedures for the handling of IT-related Reporting requests and to facilitate the processing, scheduling, coordination, documentation and improvement of all reports on IT services and infrastructure.
Reporting Management contributes to an integrated Service Management approach by achieving the following goals:
- Every authorized report facilitates the monitoring of services and service quality
- Reports facilitate the improvement of services and processes
- Reports document service delivery, service quality and service improvement
- Reports will communicate service delivery, service quality and service improvement
- Reports also ensure legal functions
- Every report runs through a set of standardized activities and procedures in order to ensure effective and efficient processing
- Every implemented Reporting is documented.
Roles & Functions
Reporting Management Specific Roles
Static Process Roles
- Reporting Process Owner
- Initiator of the process; accountable for defining the process strategic goals and allocating all required process resources. Refer to Continual Process Improvement Management for a detailed description of these activities.
- Reporting Process Manager (Reporting Manager)
- Manager of the entire process; responsible for its effectiveness and efficiency. Team leader of the function „Reporting Management Team“. Refer to Continual Process Improvement Management for a detailed description of these activities.
- Reporting Management Team
- The team associated with the Reporting Management Process.
- Senior Management
- Senior Management of the IT provider.
Dynamic Process Roles
These roles are dynamically created during the Reporting Management Process. See the process-specific or activity-specific rules for further details.
- Reporting Owner
- The attribute in the record contains the value of the Role/Function currently accountable for that Reporting (but NOT for the Reporting Management Process).
- Reporting Agent
- The attribute in the record contains the value of the Role/Function currently {responsible en} for either an activity or task within the overall activity of Reporting. The Reporting Agent can be changed with the help of a Functional Escalation, if permitted by the Rules.
- Reporting Requester (RReq)
- This is the person who triggers the creation of a report. Typically the Requester is either the:
- Process Owner
- Process Manager
- Service Owner
- Customer
- Account Manager (Customer Owner)
- Reporting Receiver (RRcv)
- This is the person or group who receives the Final Report. Typically the Receiver is either the:
- Process Owner
- Process Manager
- Service Owner
- Customer
- Account Manager (Customer Owner)
- Process Team Members
- Service Experts/Specialists
- Reporting Builder
- generates the report.
- Reporting Validator
- validates the report before it is send to the receivers.
- Reporting Data Collector
- collects and transforms the data from the live system necessary for the reporting.
Service Specific Roles
Roles depending on the affected service are found in the Service Description. The Service Description, including the service specific roles, is delivered from the Service Portfolio Management.
- Service Expert/Service Specialist
- This person has extensive knowledge about the service.
- Service Owner
- This is the person responsible for the service as defined in the Service Description.
Customer Specific Roles
Roles depending on the affected customer(s) are found in the Service Level Agreement (SLA) or Customer Record. The Service Level Agreement/Customer Record is maintained by Service Level Agreement Management / Customer Relationship Management.
- Customer(s)
- Customers of the Service
- Customer Owner
- Account Manager for the Customer
Information artifacts
This section describes information/data required or recorded by the process. In general, a Process Record (here: the Reporting Record) represents the current progress of a process and will contain all information related to the execution of that process.
Reporting Record
The Reporting Record is the record which holds management-relevant information and the history of a specific Reporting. On its creation, filled with information provided by the Report Requester. This includes:
- Unique identifier
- Reporting ID
- Reporting type
- process report – only KPIs regarding the process quality are included; service report – only KPIs regarding the service are included; mixed report – both service and process KPIs included
- Reporting requester
- Name of the Person triggering the Reporting
- Reporting Receiver
- Status
- Status of the Reporting. Is set when passing a Control Activity
- Services
- Service which is reported
- Process
- Process which is reported
- Reporting Description
- The description of the Reporting including the source of the Target Values
- Reporting Period
- Reporting Due Date
- Reporting Owner
- Reporting Agent
- Reporting sources
- Additional Remarks
- Text for additional information
- Reporting Frequency
- Reporting Priority
Forward Schedule of Reporting (FSR)
The FSR is a structured report which refers to all scheduled reports. It contains user and customer relevant information and thus offers a constricted view on all reports planned. Information that is included in the FSR is:
- Unique identifier of the Reporting
- Planned Date of Report Creation
- Description of the Reporting
- Report Receiver
- Report Requester
- Report Frequency
Accomplished Reporting Overview
The Accomplished Reporting Overview is a structured overview providing a view on all created reports. This overview should contain the following information:
- Unique identifier of the Reporting
- Date of Report Creation
- Description of the Reporting
- Report Receiver
- Report Requester
- Report Frequency
Key Concepts
Reporting Priority
Reports are classified by the following priorities:
- basic: the report need to be executed following in basic order
- superior: the report has higher priority and needs to be executed in first row
Reporting Frequency
Reports are classified by the following frequencies:
- regular: the report is executed according to a regular schedule, often on a periodical basis
- exceptional: the report is executed on exceptional basis and often is triggered by an exceptional business or service situation
Reporting Classification
Classification of reports are performed by the Reporting Management Staff in cooperation with the Service Expert/Specialist and the requester for that report. Parameters that need to be regarded are:
- Business need for a report
- Influence from preceding reports on system performance
- Resources needed to generate that report
- The current resources situation
- Side effects and the correlation of that report with other reports scheduled
Process
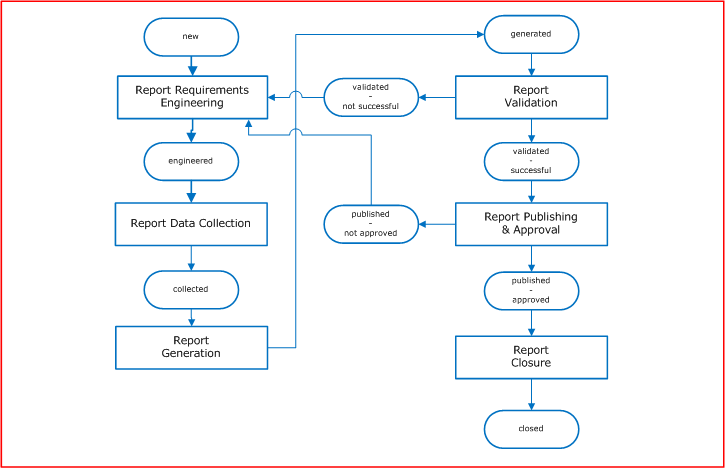
High Level Process Flow Chart
This chart illustrates the Reporting Management process and its activities. It also shows the status model reflected by the Reporting Record evolution.
Critical Success Factors
Critical Success Factors (CSF):
- Resources needed for the processing of reports
- Definition of report parameters from the business point of view
- Communication and coordination between Business and IT
- Understanding of business issues by the IT side
- Access to necessary data sources
Performance Indicators (KPI)
- Report duration time
- Number of loops between IT and business until report is approved on structure and result
- Duration of reports processing
- Divergence between real time and reported time period
- ratio between regular and exceptional report
All KPIs can measured per service, per customer, per location etc.
Process Trigger
Event Trigger
- Any request for Reporting from (these roles can act as Reporting Requestor):
- Any Process Manager or Process Owner
- Any Service Owner
- Senior Management
- Customer and Customer Owner (Account Manager)
Time Trigger
- Reports are often time triggered and processed on regular basis. Regular Reports are defined in the:
- Process Description
- Service Description
- Service Level Agreements (SLA)
- Operational Level Agreements (OLA)
- Underpinning Contracts
Process Specific Rules
- every RFR triggers the creation of a new Reporting Record
- the Reporting Agent is responsible for documenting each activity in the Reporting Record
- the Reporting Owner must control the Reporting Agent
- the Reporting Owner and Reporting Agent can only transfer their duties if the new person or group agrees
- the subsequent Reporting Owner or Reporting Agents must then be recorded in the appropriate attribute in the Reporting Record.
- the Reporting Owner and Reporting Agent should preferably be a person rather than a group.
Note: for the different types of rules refer to Rules.
Process Activities
Report Requirements Engineering
In this activity, the Reporting Agent is defined. The Report Requester details are also confirmed.
Firstly, it is checked that the Report Requester is authorized to make a request for a new, changed or existing report. If authorization is missing then the request is refused.
Diverse variables need to be taken into account when defining the report. This includes:
- business needs provided by the Business Requester
- resource availabilities of the Reporting Management Staff and Experts from Service Operations
- other reports that are scheduled to be provided by Reporting Management Staff
The report needs to use this information and define what business requirements are best. It should also take into account:
- cost of reporting
- existing resources framework
- other business requirements
The report needs to be defined, approved by the requester, tested in the test system with life data and then approved again by the requester. All the necessary processes and systems need to be instructed to collect the required data for the report.
The report then is submitted into the production system. The final approval from the requester can be provided after the first production run.
Activity Specific Rules
- Reporting Owner is set to „Reporting Management Team“ if no other person as Reporting Owner available
- Reporting Agent is set to Reporting Owner if if no ther person as Reporting Owner available
- Reporting Receiver is recorded.
- Reporting Requester is set to the person who has triggered the Reporting
- Reporting Builder is defined from the Reporting Management staff or Service Expert/Specialist Group
- Reporting Validator is defined and must be different from the Reporting Builder.
- Reporting Data Collector is defined from the Service Expert/Specialist Group
- Reporting Description must contain a meaningful description of the desired Reporting, as well as a comprehensible rationale stating the reasons for the Reporting.
- Reporting Priority is set to „standard“ if no other priority is known.
- Set Service and/or Customer and/or Process
- Set Reporting Frequency
- Set Reporting Type
- Set Reporting Period
- Set Reporting Due Date
- Define Reporting data sources
- Set Status to „engineered“
Report Data Collection
In this activity, the data is collected from various sources. This collection is then reviewed in order to determine whether it has been successful.
Activity Specific Rules
- set Reporting Agent to Reporting Data Collector
- select data from the different sources
- extract data and store it in the reporting database
- review all data – this is a plausibility check
- set status to „collected“
Report Generation
The report generation is processed by the Reporting Builder. The resulting report is then provided to the Report Validator for validation.
Activity Specific Rules
- at the beginning, the Reporting Agent is set to Reporting Builder
- the report is created out of the data in the the reporting database according to the requirements
- set Status to „generated“
Report Validation
The validation compares generated report against the requirements. The comparison may have following results:
- „validated – successful“
- „validated – not successful“
Activity Specific Rules
- the Reporting Agent is set to Reporting Validator
- perform validation against the requirements
- if the report is approved
- set Status to „validated – successful“ and continue with the next activity
- else
- document reason
- set status to „validated – not successful“
Report Publishing and Approval
The report is send to all receivers for approval and/or will be presented to the receiver. If all reporting receivers approve the report, no further actions need to be taken. If any of the receivers deny approval, the Reporting Requirements Engineering will be retriggered.
Depending on the receiver’s approval comments and the type of the report, one or more of the following processes need to be triggered:
- Contineous Process Improvement Management Process (anomalies regarding the process quality, e.g. 1st level support does not reach first resolution rate).
- Service Portfolio Management Process (e.g. anomalies as regards content of the report have been identified, for example anomalies between index values and actual values)
- Change Management Process (e.g. collect new data for next reporting period).
Note: the approval is concerning the formal report (e.g. report contains the agreed content, is presented in the agreed form etc.) and not regarding any anomalies of the reporting values.
Activity Specific Rules
- the Reporting Agent is set to Report Receivers
- Update the Report Record
- If formal criteria is not met or more information/more data for a drill-down is necessary then
- document reason for new or changed requirement
- set status to „published – not approved“
- else
- trigger processes as required for contineous improvement
- set status to „published – approved“
Report Closure
In this activity, the Reporting is documented in the Reporting Database.
Activity Specific Rules
- the Reporting Agent is set to Reporting Owner
- Update the Report Record
- Set status to „closed“